Vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs) are rechargeable batteries that store energy using a metal called vanadium. The vanadium can change into different forms to help store and release energy when needed.
Unlike traditional batteries such as lithium-ion or lead-acid, which rely on solid electrodes in a closed system, VRFBs store energy in liquid electrolytes held within external tanks. This allows for easy scaling of the battery’s energy capacity by adjusting the volume of electrolytes in the tanks.
A standout feature of VRFBs is how power and energy storage capacity are separate. Their power output is defined by the electrochemical stack, whereas their energy storage capacity is determined by the size of the external tanks. This design means VRFBs can be adjusted to meet different energy and power needs independently, making them flexible to the needs of individual projects.
Safety is another key advantage of VRFBs. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, which rely on flammable organic electrolytes, VRFBs use non-flammable aqueous solutions, reducing fire risks significantly. They also deliver high energy efficiency.
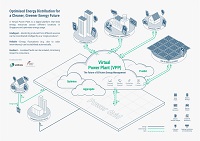
By providing long-lasting, efficient, and safe energy storage, VRFBs are an ideal solution for integrating renewable energy sources into the power grid for a stable, green energy future.